Guide to Different Types of CRM
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) software has come a long way since its much humbler beginnings. It started as little more than an expansive contact management tool, too costly for the average business, and mostly on-premise. Today, it has become an excellent marketing tool , more affordable than ever before, and primarily cloud-based. In fact, it is so expansive in its scope and capabilities that multiple different types of CRM now exist. Each such type seeks to specialize in specific functions and thus comes with different features.
What is CRM?
But first, let us briefly explore CRM as a software type, along with its core features.
True to its name, CRM software seeks to handle the set of practices known as CRM. That is, customer relationship management; the management of every interaction of a customer with a business. This scope spans across all touchpoints, from the first to the last. It thus includes all interactions in-between, from website visits to repeat purchases and customer support requests.
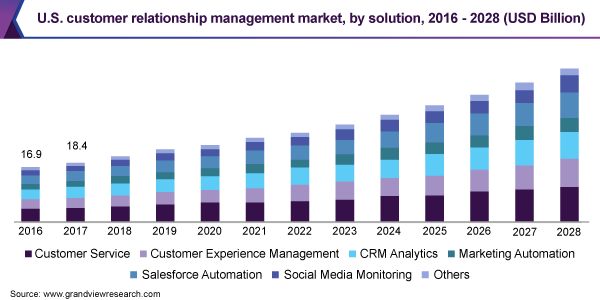
As marketing and sales digitization stride ahead, CRM became an extremely lucrative business asset. Statista finds it is the single largest software market in the world today and forecasts continued growth. GrandViewResearch agrees, finding and forecasting consistent growth among its different applications:
The core features of CRM
To achieve this purpose, CRM software typically comes with a set of core features. “Typically” needs to be stressed, as each solution will differ from the next – sometimes considerably so.
Still, these core features typically include:
- A consolidated customer database. CRM gives all departments access to one core database, breaking down data silos and facilitating easier coordination. This feature alone can offer immense help, from branding to customer service.
- Lead management tools. Such tools will include lead scoring, lead nurturing, and similar functionalities. Through them, CRM abridges the common gaps between the marketing and sales departments.
- Automation features. Finally, most CRM solutions will come with some form of automation – typically focused on sales. Such functionalities help enhance productivity and reduce time waste.
However, different businesses have different needs, so the CRM market offers different solutions to satisfy them. These manifest in various types, each with its own specialization.
The different types of CRM, and choosing the one for you
Knowing these specializations is crucial for making the ideal choice among your CRM candidates. To get the best one for your needs , you should ideally mind the following:
- Its type. The primary focus of this article, each CRM solution’s type will largely determine how well it suits your needs.
- On-premise vs. cloud-based. While most businesses now opt for cloud-based solutions, yours may need an on-premise one instead.
- GDPR compliance. As data protection regulations tighten around the world, GDPR compliance is a crucial CRM quality.
- Integrations. Your CRM solution should offer integrations with your existing assets so as to not disrupt your workflow.
- User-friendliness and onboarding. The primary issue with CRM use still lies in low adoption rates , so user-friendliness and easy onboarding are equally important.
To address the first and perhaps most crucial point, let us explore the different types of CRM. The three main ones are:
- Operational
- Analytical
- Collaborative
A fourth type comes in the form of industry-specific CRM, which takes a different approach to its features’ focus. While it is less solid and harder to define, this too will get its honorable mention below.
#1 Operational CRM
Perhaps the most popular CRM type, Operational CRM seeks to streamline operations and enhance sales. To do so, it automates processes that don’t require creative input, and typically offers the following types of features:
- Service automation. As swift, efficient customer service is pivotal to any business, this set of features enhances it by automating communication alerts. This allows for appropriate agents to quickly respond to customer requests, while also having relevant historical information in hand as they do.
- Marketing automation. Instead, such features hinge on collecting customer data across various touchpoints, from emails to website behavior and more. They then generate reports on such metrics, informing marketing decisions and outreach. Perhaps most notably, such features can inform cross-sell and upsell offers for recurring customers.
- Sales automation. Similarly, sales automation features automate sales outreach to qualified leads. Especially in tandem with thorough lead scoring, such features can minimize ineffective outreach and save sales representatives valuable time.
Perhaps the most notable example of Operational CRM at work is email marketing automation. Through it, businesses can set event triggers for maximum email effectiveness, automate outreach at specific intervals, or both.

#2 Analytical CRM
Another popular type is Analytical CRM. Among the different types of CRM, Analytical is the most analytical-minded – as the name implies. It thus thrives on customer analytics and insights and can inform anything from lead acquisition strategies to sales tactics.
Its typical features include:
- Deeper customer segmentation. Such CRM solutions will offer to segment customers according to a business’s ideal criteria, along the lines of demographics, psychographics, location, interaction history, and more. They can thus enhance outreach effectiveness to individual segments and fine-tune marketing strategies to them.
- Predictive modeling. In conjunction, predictive modeling allows such solutions to combine customer data with such external factors as holidays, the weather, and more, and produce accurate forecasts. Businesses may use such insights to inform sales goals, adjust product availability plans, and more.
- Profitability analysis. Finally, profitability analysis allows for value-based customer segmentation. Such features weigh customers’ profitability against their outreach and retention costs, helping to further improve sales outreach and prioritization.
While not as prevalent as Operational CRM, this type offers invaluable insights regarding customer segmentation and profitability.

#3 Collaborative CRM
The third and final among the different types of CRM comes with Collaborative CRM. This one, also true to its name, focuses primarily on enhancing internal collaboration and streamlining communications.
To do so, it offers such features as:
- Interaction management. Such solutions will track customer interactions with your business and relay this information to all relevant departments. This, too, helps departments coordinate, as well as identify recurring requests that may be addressed in a timely manner.
- Channel management. Similarly, channel management features consolidate all communication channels under one dashboard for enhanced efficiency and better response times. This can include customer inquiry platforms, such as social media and email, as well as internal communication channels.
- Document management. Finally, such solutions will often offer document management and sharing options. Such features will help ensure no crucial documents are lost or mismanaged, further reducing the room for error that may cost a conversion.
Should a business struggle with communications and cross-department time management, Collaborative CRM may warrant their attention.

#4 Industry-specific CRM
Finally, a subtype of CRM comes in the form of industry-specific CRM – as opposed to general-use CRM. Such CRMs will focus on the work environment and specific needs of one industry and fine-tune their features accordingly. As such, you may see Automotive CRM, Restaurant CRM, Healthcare CRM, and so forth.
This type focuses on its selection of features rather than on an explicit functionality focus. Thus, such CRM solutions do offer some notable benefits through industry-specific features, like:
- Electronic Health Record (EHR) systems for healthcare professionals
- Dealer Management Systems (DMS) for automotive dealerships
- Listing management tools for real estate agencies
However, many such solutions may also come with such limitations and drawbacks as:
- A specialization premium
- Lack of flexibility
- A focus on feature specificity over quality or ease of use
That’s not to say industry-specific CRM may not offer a great business asset, by all means. It’s only to say that “horizontal” CRMs may still offer a better alternative, depending on your specific CRM candidates. Still, such businesses as restaurants may value reservation systems and POS integrations highly – which general-use solutions may lack.

The post Guide to Different Types of CRM appeared first on Olive Street Design.



















